Searching for today’s Syntax Verse Daily Quiz Answer 4 January 2026? End your search here, collect your rewards of Today Syntax Verse Quiz “Why do some protocols use upgradeable smart contracts?” with QuikNotes.
About Syntax Verse:
Syntax Verse: Web3 Mining Project to Earn $SYNTAX Tokens
Syntax Verse is an innovative Web3 mining project that launched on March 17, 2025, offering users the opportunity to earn $SYNTAX cryptocurrency tokens. The platform has quickly attracted a growing community of over 50,000 users.
Available on Android and iOS
Syntax Verse provides dedicated apps for both Android and iOS devices, making it easy to mine and manage your tokens on the go. You can download the Syntax Verse app directly from the Google Play Store and App Store.
Here are Syntax Verse Daily Quiz Answer 4 January 2026:
- Quiz: Why do some protocols use upgradeable smart contracts?
- Answer: B) To allow improvements or fixes without deploying a new contract.
Syntax Verse Daily Vault Pattern Code 4 January 2026:
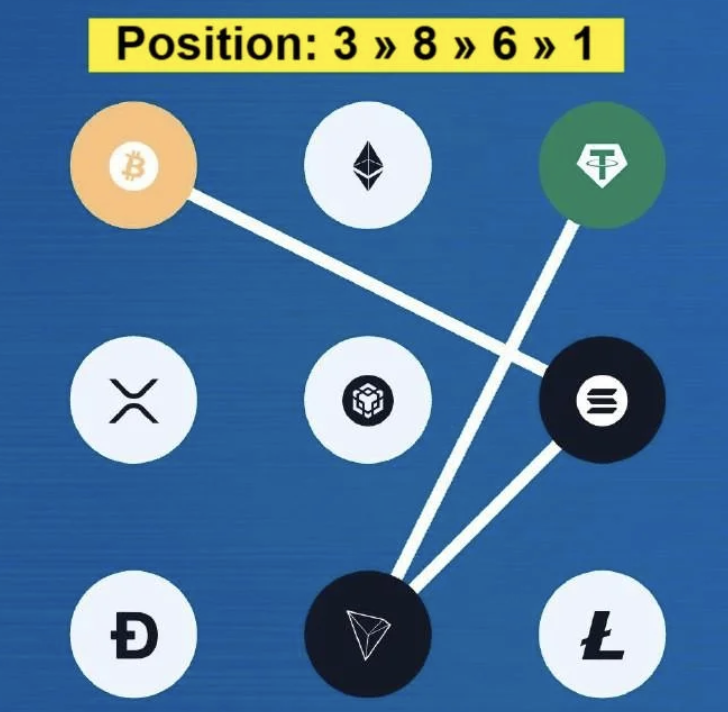
Syntax Verse Daily General Quiz Answer
ERC-721 Token (NFT Standard)
- Question 1: What does the ERC-721 standard primarily define?
Answer: C) Non-fungible tokens on Ethereum. - Question 2: Which characteristic best distinguishes ERC-721 tokens from ERC-20 tokens?
Answer: A) Each token has a unique identifier. - Question 3: What function is used in ERC-721 to check who owns a specific token?
Answer: B) ownerOf(). - Question 4: Which use case is MOST commonly associated with ERC-721 tokens?
Answer: C) Digital collectibles and NFTs. - Question 5: Which statement about ERC-721 tokens is TRUE?
Answer: D) Each token represents a distinct asset.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Question 1: What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes a decentralized exchange (DEX) from a centralized exchange (CEX)?
Answer: C) DEXs allows peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. - Question 2: Which of the following is a popular decentralized exchange on Ethereum?
Answer: D) Uniswap. - Question 3: What mechanism do many DEXs use instead of traditional order books?
Answer: B) Automated Market Makers (AMMs). - Question 4: In AMM-based DEXs, liquidity providers deposit tokens into what structure?
Answer: A) Liquidity pools.
Lending Protocols in DeFi
- Question 1: Which DeFi protocol is widely known for introducing the concept of overcollateralized crypto lending?
Answer: C) Aave. - Question 2: What is the main purpose of collateral in DeFi lending protocols?
Answer: A) Protecting lenders from borrower default. - Question 3: In many lending protocols, what happens if the collateral value falls below a required threshold?
Answer: C) Liquidation occurs. - Question 4: Which type of interest rate model is commonly used in DeFi lending protocols?
Answer: C) Variable and utilization-based. - Question 5: What does “TVL” stand for in the context of lending protocols?
Answer: B) Total Value Locked.
Impermanent Loss
- Question 1: What is the primary cause of impermanent loss in liquidity pools?
Answer: B) Price divergence between paired assets. - Question 2: Impermanent loss occurs most commonly in which type of DeFi system?
Answer: D) AMM-based liquidity pools. - Question 3: Which liquidity pair is least likely to experience high impermanent loss?
Answer: C) USDC-USDT. - Question 4: Impermanent loss becomes permanent when the liquidity provider does what?
Answer: D) Withdraws funds from the pool.
Liquidity Mining Pools
- Question 1: What is the primary purpose of a liquidity mining pool?
Answer: C) To supply liquidity for trading on a decentralized exchange. - Question 2: What do liquidity providers typically receive in exchange for depositing tokens into a liquidity pool?
Answer: A) LP tokens. - Question 3: Which pair of assets would most likely be found in an AMM-style liquidity pool?
Answer: A) ETH & USDC. - Question 4: What is “impermanent loss” in liquidity mining?
Answer: D) A temporary reduction in potential earnings due to price divergence.
Interoperability in Blockchain
- Question 1: What does blockchain interoperability primarily enable?
Answer: B) Different blockchains to exchange data and assets. - Question 2: Which technology is central to enabling communication between different blockchain networks?
Answer: A) Interledger protocols. - Question 3: Polkadot uses what component to connect multiple specialized blockchains?
Answer: C) Parachains. - Question 4: What does the Cosmos ecosystem use to achieve interoperability?
Answer: D) IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication).
Hard Fork vs Soft Fork
- Question 1: Which statement best describes a hard fork?
Answer: ✅ A) A change that requires all nodes to upgrade to remain valid. - Question 2: Which statement best describes a soft fork?
Answer: ✅ D) A backward-compatible change. - Question 3: What typically happens if a hard fork is contentious and not everyone agrees?
Answer: ✅ A) A new, separate blockchain may form. - Question 4: Which of the following is required for a soft fork to succeed?
Answer: ✅ C) A majority of miners must enforce the new rules. - Question 5: Which fork type can introduce stricter rules while remaining compatible with older software?
Answer: ✅ B) Soft fork.
Blockchain Explorer System
- Question 1: What is the main purpose of a blockchain explorer?
Answer: B) To view blockchain data. - Question 2: Which of the following can you typically not find on a blockchain explorer?
Answer: D) Private keys. - Question 3: What does a transaction “hash” represent in a blockchain explorer?
Answer: C) A unique ID for the transaction. - Question 4: What does “block height” refer to in a blockchain explorer?
Answer: C) The position of a block in the chain.
DeFi vs Traditional Finance System
- Question 1: Which feature best differentiates DeFi from traditional finance?
Answer: D) Permissionless access - Question 2: In traditional finance, who typically controls user funds?
Answer: A) Third-party intermediaries - Question 3: What enables DeFi protocols to operate without centralized management?
Answer: C) Smart contracts - Question 4: Which of the following is a major advantage of DeFi over traditional finance?
Answer: C) Global accessibility - Question 5: What aspect of DeFi allows users to keep full control of their assets?
Answer: B) Self-custody wallets
Consensus Mechanism Systems
- Question 1: Which consensus mechanism does Bitcoin use?
Answer: A) Proof of Work - Question 2: What is the main purpose of a consensus mechanism in blockchain?
Answer: C) To agree on valid transactions - Question 3: Which consensus mechanism relies on validators staking their coins to participate?
Answer: C) Proof of Stake - Question 4: In Proof of Work, what do miners mainly compete for?
Answer: B) Solving cryptographic puzzles
FUD in Crypto Market
- Question 1: What does the term “FUD” stand for in the crypto market?
Answer: ) Fear, Uncertainty, and Doubt - Question 2: Which of the following is a common effect of FUD in the crypto market?
Answer: B) Panic selling by investors - Question 3: FUD is often spread intentionally to:
Answer: D) Manipulate market prices - Question 4: Which of the following news headlines is MOST likely an example of FUD?
Answer: B) “Major exchange hacked; millions at risk!”
Gas in the Ethereum network
- Question 1: What does “gas” primarily measure in the Ethereum network?
Answer: C) Computational work required for a transaction. - Question 2: What happens if a transaction runs out of gas before it completes?
Answer: A) It fails and still consumes the gas provided. - Question 3: Which unit is gas price usually measured in?
Answer: B) Gwei. - Question 4: What determines how quickly a transaction gets picked up by validators?
Answer: D) Gas price.
Honeypots in Crypto
- Question 1: What is a honeypot in cryptocurrency?
Answer: A) A smart contract designed to trap users into losing funds. - Question 2: What makes a honeypot token appear attractive to buyers?
Answer: B) Rapid price increase and active marketing. - Question 3: In a typical honeypot scam, what can the victim usually not do?
Answer: D) Sell the token they just bought. - Question 4: Which blockchain platform is most commonly targeted with honeypot tokens?
Answer: D) Binance Smart Chain (BSC).
Understanding Miner Block Manipulation
- Question 1: What does “block manipulation” generally refer to in cryptocurrency mining?
Answer: A) Influencing which transactions go into a block. - Question 2: What allows miners to choose which transactions to include in the next block?
Answer: A) Their computational power. - Question 3: Why might miners reorder transactions in a block?
Answer: C) To maximize their own profit. - Question 4: Which term refers to miners intentionally reordering transactions to gain profit from price differences?
Answer: D) MEV (Miner Extractable Value).
Centralized Exchanges Storage Risks
- Question 1: When you store your crypto on a centralized exchange, who technically controls your private keys?
Answer: C) The exchange. - Question 2: What common phrase summarizes the risk of not controlling your own wallet keys?
Answer: B) “Not your keys, not your coins.” - Question 3: Which major exchange collapse in 2022 highlighted the dangers of leaving funds on centralized platforms?
Answer: D) FTX. - Question 4: Why can withdrawals sometimes be halted on centralized exchanges?
Answer: A) Because the exchange may be facing liquidity issues.
PoW vs PoS
- Question 1: What is the main reason Proof of Work (PoW) is considered more reliable than Proof of Stake (PoS)?
Answer: B) It has been tested and proven secure for over a decade. - Question 2: In PoW, what do miners compete to solve in order to add a new block?
Answer: A) Cryptographic puzzles. - Question 3: What is one major concern with Proof of Stake systems?
Answer: D) Risk of centralization by wealthy participants. - Question 4: What percentage of mining power would an attacker need to control to compromise a PoW network?
Answer: A) 50%.
Type of Bitcoin Wallet Addresses
- Question 1: Which of the following is the original format of Bitcoin wallet addresses?
Answer: B) P2PKH. - Question 2: What prefix do P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash) addresses typically start with?
Answer: C) 3. - Question 3: Bech32 addresses are also known as what type of Bitcoin addresses?
Answer: D) SegWit. - Question 4: Which Bitcoin address type is considered most efficient in terms of block space usage?
Answer: C) Bech32. - Question 5: Which Bitcoin address type is best suited for modern wallet compatibility and lowest fees?
Answer: B) Bech32.
Check More Question & Answers: Check Now
Earn Extra $SYNTAX with Quizzes
Two standout features of the platform are the Daily Quiz and the General Quiz, where users can earn free $SYNTAX tokens by completing daily and general quiz challenges. These quizzes make the mining experience more fun and rewarding.
Get Daily Updates On Telegram – Join Now
Want to join Syntax Verse: Join Now
Stay Tunned
Keep you up with the latest in gaming, entertainment, general news, puzzles, technology, and more. Our detailed roundup of recent articles covers a broad spectrum of subjects, providing you with both information and entertainment on diverse topics. Stay informed and engaged with a variety of interests through our comprehensive updates.
Red Packet: 2DUDNJME
